Finite Element Analysis (Structural)
The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a numerical method for solving problems of engineering and Structural Analysis of buildings, bridges, warehouses, etc.
Finite element analysis FEA is helpful for problems with complicated geometries, loadings, and material properties where analytical solutions can not be obtained.
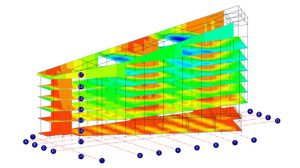
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) or Finite Element Method (FEM).
The Purpose of FEA Analytical is to have Solutions for following:
• Stress analysis for trusses, beams, and other superficial structures is carried out based on dramatic simplification
and idealization:
– mass concentrated at the center of gravity
– beam simplified as a line segment (same cross-section)
• Design is based on the calculation results of the idealized
structure & a significant safety factor (1.5-3) given by experience.
• Design geometry is a lot more complex and requires much higher accuracy. We need to understand the physical behaviors of a complex object (strength, heat transfer capability, fluid flow, etc.)
– To predict the performance and behavior of the design; to calculate the safety margin; and to identify the weakness of the design accurately; and
– To identify the optimal design with confidence
Brief History of Finite Element Analysis (FEA).
Grew out of the aerospace industry
Post-WW II jets, missiles, space flight
Need for lightweight structures
Required accurate stress analysis
Paralleled growth of computers
Common FEA Applications
Mechanical/Aerospace/Civil/Automotive
Engineering
Structural/Stress Analysis
Static/Dynamic
Linear/Nonlinear
Fluid Flow
Heat Transfer
Electromagnetic Fields
Soil Mechanics
Acoustics
Biomechanics
Complex Object Simple Analysis
(Material discontinuity,
Complex and arbitrary geometry) Discretization
Real World
Simplified (Idealized)
Physical Model
Mathematical Model
Discretized (mesh)
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computational technique used to simulate and predict the behavior of physical systems by breaking them down into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements. This method is widely used in engineering and mathematical modeling to solve problems related to:
- Structural analysis
- Heat transfer
- Fluid flow
- And more
The Finite Element Method (FEM), the mathematical foundation of FEA, subdivides a large system into smaller elements, creating a mesh. Each element is analyzed individually, and the results are combined to understand the overall behavior of the system.
Finite Element Analysis
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computational technique used to simulate and predict the behavior of physical systems by breaking them down into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements. This method is widely used in engineering and mathematical modeling to solve problems related to:
- Structural analysis
- Heat transfer
- Fluid flow
- And more
The Finite Element Method (FEM), the mathematical foundation of FEA, subdivides a large system into smaller elements, creating a mesh. Each element is analyzed individually, and the results are combined to understand the overall behavior of the system .
Definition and Principles
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computational technique used to simulate and predict the behavior of physical systems. It involves breaking down a complex system into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements, which are then analyzed using differential equations. This method is widely used in engineering and mathematical modeling to solve problems related to structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, and more .
The Finite Element Method (FEM), the mathematical foundation of FEA, subdivides a large system into smaller elements, creating a mesh. Each element is analyzed individually, and the results are combined to understand the overall behavior of the system. This approach allows for accurate representation of complex geometries and material properties .
FEA is essential in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering, as it helps optimize designs, reduce the need for physical prototypes, and save time and resources. By simulating real-world conditions, engineers can make informed decisions and improve the safety and performance of their designs .
Basic Concepts
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a numerical method used to solve complex engineering and mathematical problems. It involves subdividing a large system into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements, which are then analyzed to approximate the behavior of the entire system. FEA is widely used in structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, and electromagnetic potential . The process begins with creating a mesh of the object, which represents the numerical domain for the solution. This mesh is composed of numerous small elements, and the method approximates the unknown function over the domain by minimizing an associated error function .
The Policy of New Condominium Safety Law
Policy changes in new condominium safety law from Senate Bill 4-D will focus on more extraordinary, significant, and recurrent inspection processes. With the help of Florida condominium engineers, the bill was written to ensure that condominium buildings are properly maintained as they age.
The bill requires condominium associations and developers to set aside funds to cover structural safety inspections of any three stories or taller buildings throughout Florida and keep enough funds for repairs when necessary. This will ensure no shortcuts are taken due to inadequate budgeting or funding. These reserves must be reassessed every ten years to cover high maintenance costs.
Senate Bill 4-D also requires mandatory statewide inspections through a new program. A condo building taller than three stories requires one assessment every decade after its certificate of occupancy reaches 30 years of age. The bill requires condominium and cooperative associations to conduct a “structural integrity reserve study” that includes waterproofing, exterior painting, the roof, load-bearing walls, floor, foundation, fireproofing and fire protection systems, plumbing, and any item with deferred maintenance or replacement cost that exceeds $10,000.
Condominiums that are located within three miles of the Florida coast require inspections known as “milestone inspections.” These inspections must begin after 25 years of building occupancy and every ten years thereafter.
All inspection reports must also be published online and shared with owners and tenants. If an inspection uncovers a need for any structural repairs or maintenance, this work must be performed within a year following the report.
How Change Will Help
Call EMA Engineers to schedule your structural inspections of your condominium buildings at (321) 355-6052 or visit us at https://forensicengineerflorida.com
https://foursquare.com/v/ema-structural-forensic-engineers/57f74f03498ecadc37a97b4a
https://www.zipleaf.us/Companies/EMA-Structural-Forensic-Engineers_24125
